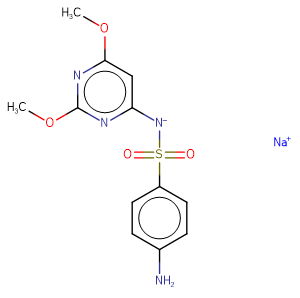
SulfadiMethoxine sodium
CAS No. 1037-50-9
SulfadiMethoxine sodium( —— )
Catalog No. M21172 CAS No. 1037-50-9
Sulfadimethoxine is a antimicrobial agent treatment of respiratory urinary tract enteric and soft tissue infections.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | 52 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | 68 | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameSulfadiMethoxine sodium
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionSulfadimethoxine is a antimicrobial agent treatment of respiratory urinary tract enteric and soft tissue infections.
-
DescriptionSulfadimethoxine is a antimicrobial agent treatment of respiratory urinary tract enteric and soft tissue infections.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayMicrobiology/Virology
-
TargetAntifection
-
RecptorAntifection
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1037-50-9
-
Formula Weight332.31
-
Molecular FormulaC12H13N4NaO4S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:66 mg/mL (198.6 mM)
-
SMILESCOc1cc([N-]S(=O)(=O)c2ccc(N)cc2)nc(OC)n1.[Na+]
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference



-
Desmethylbellidifoli...
Desmethylbellidifolin is a natural xanthone extracted from Gentianella acuta.?1,3,5,8-Tetrahydroxyxanthone has antispasmodic effect and anti-inflammatory activity.?
-
Niranthin
Niranthin is a potent anti-leishmanial agent, inhibits the relaxation activity of heterodimeric type IB topoisomerase of L. donovani and acts as a non-competitive inhibitor interacting with both subunits of the enzyme. Niranthin also exhibits anti-hepatitis B virus, antiinflammatory and antiallodynic actions.
-
Altenuene
Altenuene is a mycotoxin, it frequently occurs in food and feed items infested by fungi of the genus Alternaria. Altenuene demonstrates moderate activity against Staphylococcus aureus. Altenuene also exhibits cytotoxic activity against lung cancer cell line A549, breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231 and pancreatic cancer cell line PANC-1.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


